Objective: Diversity of cultural expression to be appreciated
Outcome: Diversity of cultural expression is appreciated
Measure: Diversity of cultural expression appreciated
Short description
By an appreciation of the diversity of cultural expression, we mean valuing the different ways people express themselves through diverse cultural forms, reflecting their life experience and interests.
Full description and underpinning theory
Full description
This outcome is about the appreciation of diverse and different forms of cultural expression that can result from engagement. Appreciation is defined here as the recognition or understanding of the worth, value or quality of form/s of cultural expression, including new forms of cultural expression generated when diverse cultures come together. Cultural expression is defined as the different ways that people express themselves depending on their cultural backgrounds, life experience and interests. Thus a culture might be related to ethnic, linguistic, religious or national heritage, but also through identification with others who share expressive interests, such as people who have a shared experience of disability that they seek to express, or expertise in a particular art form or type of cultural expression, such as hiphop, emo or contemporary painting.
This is related to the contribution of this diversity to quality of life and life choices, and the way that people connect with others through this expression. The total amount or percentage of cultural diversity is not the endpoint, but the appreciation of the existing diversity, as well as appreciation of the new forms of cultural expression that are generated when diverse cultures come together. This outcome corresponds closely to UCLG’s cultural element of ‘diversity’, which is seen as “a means to achieve a more satisfactory intellectual, emotional, moral and spiritual existence” (UCLG, 2006, p. 5).
Theory underpinning this outcome
Hawkes talks about the vital contribution of cultural diversity; “just as biodiversity is an essential component of ecological sustainability, so is cultural diversity essential to social sustainability. Diverse values should not be respected just because we are tolerant folk, but because we must have a pool of diverse perspectives in order to survive, to adapt to changing conditions, to embrace the future. And it is not simply the discourse between diverse values that will stimulate our communities to discover new visions. The diversity of mediums of expression and of cultural manifestations are both essential parts of life’s rich tapestry and invaluable tools with which to engage with the challenges that will inevitably confront us” (Hawkes, 2001, p. 12).
Cultural diversity is integral to social cohesion, human development, peaceful coexistence and the prosperity of societies (International Network on Cultural Policy, 2000).
Appreciation of diversity is related to cultural rights, which are an integral part of human rights. “No one may invoke cultural diversity to infringe upon the human rights guaranteed by international law, nor to limit their scope.; enhanced empathy of other cultures (UCLG, 2006):
engaging diverse communities of interest in the creation of new work (Arts Victoria 2013).
Diversity: respecting and interacting with cultural diversity makes the arts more relevant, dynamic, innovative and reflective of Australia today; inclusiveness: exploring each other’s cultures through making art encourages mutual respect and social harmony (Australia Council for the Arts, 2016; McCarthy et al, 2004; UNESCO, 1998).
Evidence that this outcome occurs
Community celebrations encourage valuing of diversity (Hilbers 2012); 62% of respondents agree that the arts “helps me understand other cultures better” (Americans for the Arts, 2015).
Activities contributing to this outcome
Activities
As of April 2021, there were 37 activities in Takso selecting this outcome with 9 completed and evaluated. Types of activities undertaken to achieve this outcome include:
- Commissioning of public art (not acquired)
- Exhibitions: of arts and objects in all forms
- Gathering, celebration or ceremony
- Performances: performing arts all forms
Results
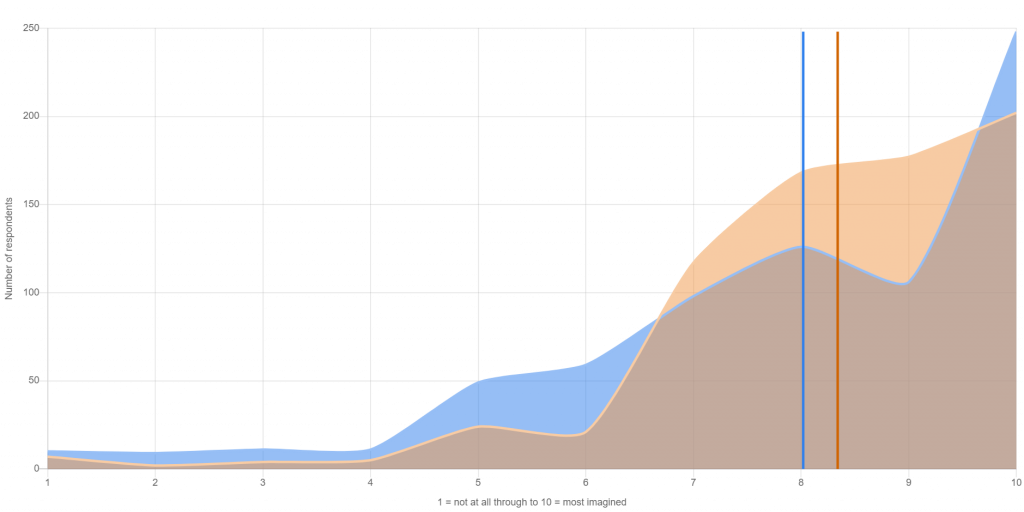
Over the 9 completed activities that addressed this outcome, 727 people responded to the evaluation question. On a scale of 1 to 10, with 1 being not at all and 10 the most imaginable, respondents reported an average pre activity level of 8 for this outcome and a post activity attainment of 8.4.
Diversity of cultural expression appreciated
9 activities / 727 responses / Pre activity average 8.0 / Post activity average 8.4
Evaluation measure
Appreciation of diversity of cultural expression.
References
Arts Victoria (2013). OIP Assessment Framework. Melbourne: Arts Victoria.
Australia Council for the Arts (2016). Cultural engagement framework. Sydney: Australia Council for the Arts. Accessed 28 May 2016 from www.australiacouncil.gov.au/about/cultural-engagement-framework/.
Hawkes, J. (2001). The Fourth Pillar of Sustainability. Melbourne: Cultural Development Network.
International Network on Cultural Policy (2000). 3rd Annual Ministerial Meeting of the International Network on Cultural Policy.
McCarthy, K., Ondaatje, E., Zakaras, L., & Brooks, A. (2004). Gifts of the Muse: Reframing the debate about the benefits of the arts. USA: RAND Corporation. Retrieved 20 December, 2009 from www.rand.org/pubs/monographs/2005/RAND_MG218.sum.pdf.
United Cities and Local Governments (UCLG) (2006). Agenda 21 for Culture. Barcelona: UCLG. Retrieved from http://www.agenda21culture.net/documents/agenda-21-for-culture
UNESCO (1998). Action plan to place culture at the heart of development, the Intergovernmental Conference on Cultural Policies for Development, Stockholm, http://www.unesco-sweden.org/conference/action_plan.htm

